Materials Used in High-Temperature Labels
High-temperature labels are essential in industries where standard labelling materials would degrade, melt or lose adhesion due to heat.
These specialist labels are designed to remain intact and readable even when exposed to extreme temperatures, making them critical in sectors such as electronics manufacturing, aerospace, automotive, metal processing and sterilisation environments.
The materials used in these labels are carefully selected to withstand both direct heat and the stresses that come with high-temperature operations.
1. Substrate Materials
The most important component of a high-temperature label is the substrate. This is the base material onto which print is applied. Common materials include:
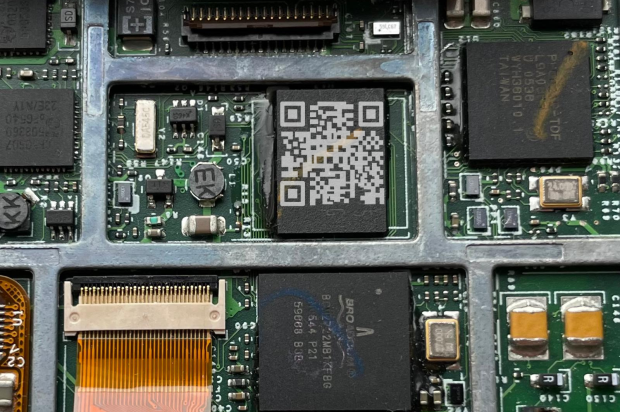
Polyimide: Known for its excellent thermal stability. Polyimide films (such as Kapton®) are widely used in electronics manufacturing, especially during the soldering process. They can withstand temperatures up to around 350°C and even higher for short bursts. Polyimide also resists chemicals, abrasion and UV exposure, making it ideal for harsh environments.
Polyester (PET): While not as heat resistant as polyimide, treated polyester labels can endure temperatures of up to 150–250°C, depending on the formulation. They are more cost-effective and suitable for less extreme applications such as autoclave sterilisation or low-heat industrial processes.
Aluminium Foil: Labels made with an aluminium base and coated with an inorganic top layer can endure temperatures of 500–600°C. These are often used in metal processing or aerospace settings where heat exposure is intense and prolonged.
Ceramic-Coated Films: In highly specialised cases, ceramic-coated polymer films can withstand extreme temperatures of up to 1250°C. These are used in environments like furnaces or high-heat testing chambers.
2. Adhesives
Even the best label substrate is useless without a suitable adhesive. In high-temperature environments, the adhesive must bond firmly to surfaces without degrading.
Silicone Adhesives: Silicone is the most common choice for high-heat applications. It performs well at elevated temperatures and maintains adhesion over time, even after repeated heating and cooling cycles.
Acrylic Adhesives: High-performance acrylic adhesives can also withstand elevated temperatures (up to around 200°C), especially when enhanced with heat stabilisers. They offer a good balance of performance and affordability in moderate heat settings.
3. Top Coats and Print Compatibility
Many high-temperature labels come with a specially treated topcoat that allows for thermal transfer printing. This method uses heat and a resin-based ribbon to print durable information onto the label. Resin ribbons are required to ensure the print itself doesn’t degrade under high heat.
Conclusion
Choosing the right materials for high-temperature labels depends on the specific application and exposure conditions. Polyimide offers high heat resistance for electronics, while polyester is suitable for lower temperature needs. Aluminium and ceramic-coated labels serve ultra-high heat applications. Paired with the right adhesive and print method, these materials ensure labels remain legible and firmly attached, even under the toughest conditions.
- Barcode Labels
- BarTender Label Design & Print Software
- Biodegradable Labels
- Block Out Labels
- Booklet and Fold out Labels
- Cryogenic Labels
- Fan-Fold Labels
- High Temperature Heat-Proof Labels and Tags
- Label Design and Print Software
- Loop Lock Labels
- Peel and Reveal Labels
- PiggyBack Labels
- RFID and Security Labels
- Security Labels
- Sustainable Labels
Get a Free Sample Pack
-
Our Products -
More Products